How to use Proxmox as ZFS Storage and VM Server
There are not too many Linux distributions that include ZFS per default. The two main options are TrueNAS Scale and Proxmox.
One is a NAS distribution where you should not do anything outside the web-gui and the other has a strong focus on virtualisation.
While I would not suggest to install complex applications on Proxmox directly, I see no problem to enable the two kernelservices kernel-smbd and kernel-nfs. This allows Proxmox to act as NFS and SMB server, with the RDMA capable ksmbd even much faster than the usual SAMBA SMB server. For a typical Storageserver you mainly need NFS and SMB.
Steps to use Proxmox as NAS after installing a default Proxmox
1. Setup kernelbased ksmbd SMB direct server at console as root (high performance, RDMA capable)
apt install ksmbd-tools
modprobe ksmbd
Then create /etc/ksmbd/ksmbd.conf (SAMBA smb.conf alike settings, anonymous access), use WinSCP
[global]
unix charset = UTF-8
workgroup = WORKGROUP
server string = SMB-Server
guest account = nobody
create mask = 0775
directory mask = 0755
browsable = yes
map to guest = bad user
# optionally add shares
[share_example]
guest ok = yes
path = /tmp
Start/Stop ksmbd SMB server
systemctl stop ksmbd
systemctl start ksmbd
systemctl restart ksmbd
remove SAMBA if installed:
systemctl stop samba
apt remove samba
1. Setup kernelbased NFS server at console as root
apt install nfs-kernel-server
Configure NFS share in /etc/exports (for folder /tmp)
/tmp ´*(rw,sync,no_subtree_check)
Start NFS Server
systemctl start nfs-kernel-server
systemctl enable nfs-kernel-server
restart on new settings in /etc/exports
systemctl restart nfs-kernel-server
1. Web-Gui
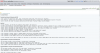
Proxmox comes with a web-Gui with advanced VM options but with only very basic ZFS management options.
For advanced ZFS managent you can add one of the web-gui add-ons like my napp-it or Poolsman
Napp-it is a web-gui that runs on Windows 11/Windows Server without installation.
download https://www.napp-it.org/doc/downloads/xampp.zip and unzip \xampp to c:\xampp (free for noncommercial use)
and start the web-gui „C:\xampp\__start_zfs-gui_as_admin.bat“ as admin, connect via browser and https://localhost
To manage Proxmox remotely from Windows
Use WinSCP to upload „C:\xampp\web-gui\data\cs_server\“ to /var/web-gui.
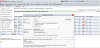
Add the remote Server in the web-gui in menu ZFS Servergroup with an access key
Enter access key to /var/web-gui/cfg/server.auth
Start remotecontrol app as root on console: perl /var/web-gui/cs_server/start_server_as_admin.pl
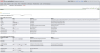
In napp-it cs, you can now select the Proxmox server and manage just like the local Windows ZFS and Storage Spaces server.
Napp-it can manage ZFS, snaps, replications and NFS or SMB shares
There are not too many Linux distributions that include ZFS per default. The two main options are TrueNAS Scale and Proxmox.
One is a NAS distribution where you should not do anything outside the web-gui and the other has a strong focus on virtualisation.
While I would not suggest to install complex applications on Proxmox directly, I see no problem to enable the two kernelservices kernel-smbd and kernel-nfs. This allows Proxmox to act as NFS and SMB server, with the RDMA capable ksmbd even much faster than the usual SAMBA SMB server. For a typical Storageserver you mainly need NFS and SMB.
Steps to use Proxmox as NAS after installing a default Proxmox
1. Setup kernelbased ksmbd SMB direct server at console as root (high performance, RDMA capable)
apt install ksmbd-tools
modprobe ksmbd
Then create /etc/ksmbd/ksmbd.conf (SAMBA smb.conf alike settings, anonymous access), use WinSCP
[global]
unix charset = UTF-8
workgroup = WORKGROUP
server string = SMB-Server
guest account = nobody
create mask = 0775
directory mask = 0755
browsable = yes
map to guest = bad user
# optionally add shares
[share_example]
guest ok = yes
path = /tmp
Start/Stop ksmbd SMB server
systemctl stop ksmbd
systemctl start ksmbd
systemctl restart ksmbd
remove SAMBA if installed:
systemctl stop samba
apt remove samba
1. Setup kernelbased NFS server at console as root
apt install nfs-kernel-server
Configure NFS share in /etc/exports (for folder /tmp)
/tmp ´*(rw,sync,no_subtree_check)
Start NFS Server
systemctl start nfs-kernel-server
systemctl enable nfs-kernel-server
restart on new settings in /etc/exports
systemctl restart nfs-kernel-server
1. Web-Gui
Proxmox comes with a web-Gui with advanced VM options but with only very basic ZFS management options.
For advanced ZFS managent you can add one of the web-gui add-ons like my napp-it or Poolsman
Napp-it is a web-gui that runs on Windows 11/Windows Server without installation.
download https://www.napp-it.org/doc/downloads/xampp.zip and unzip \xampp to c:\xampp (free for noncommercial use)
and start the web-gui „C:\xampp\__start_zfs-gui_as_admin.bat“ as admin, connect via browser and https://localhost
To manage Proxmox remotely from Windows
Use WinSCP to upload „C:\xampp\web-gui\data\cs_server\“ to /var/web-gui.
Add the remote Server in the web-gui in menu ZFS Servergroup with an access key
Enter access key to /var/web-gui/cfg/server.auth
Start remotecontrol app as root on console: perl /var/web-gui/cs_server/start_server_as_admin.pl
In napp-it cs, you can now select the Proxmox server and manage just like the local Windows ZFS and Storage Spaces server.
Napp-it can manage ZFS, snaps, replications and NFS or SMB shares

Last edited: